The Eswatini Communications Commission is the regulatory body responsible for regulating the communications sector in Eswatini, constituting of telecommunication services and networks, broadcasting services, postal services and the use and allocation of radio spectrum. It derives its mandate from the Swaziland Communications Commission Act no. 10 of 2013.
The Commission became operational on the 31st July 2013, effectively taking over all the regulatory powers of the sector from the Eswatini Posts and Telecommunications Corporation (EPTC) and Eswatini Television Authority (Eswatini TV).
The aim of a regulator is to ensure that the sector is working properly, and that consumer and other stakeholder interests are protected in a fair and balanced manner. An effective regulator is the vehicle to ensure credible market entry, as well as compliance with and enforcement of existing regulations. To achieve this, governments must create and maintain an environment conducive to good governance and regulatory success. Independence is a critical attribute for a regulator to be effective. Effectiveness, however, has additional dimensions. In a broad sense, an effective regulator is structurally and financially independent, but the real effectiveness of the regulator will depend on how it achieves successful functionality, ideally in an independent and autonomous manner. In addition, an effective regulator should demonstrate other characteristics, including accountability, transparency and predictability
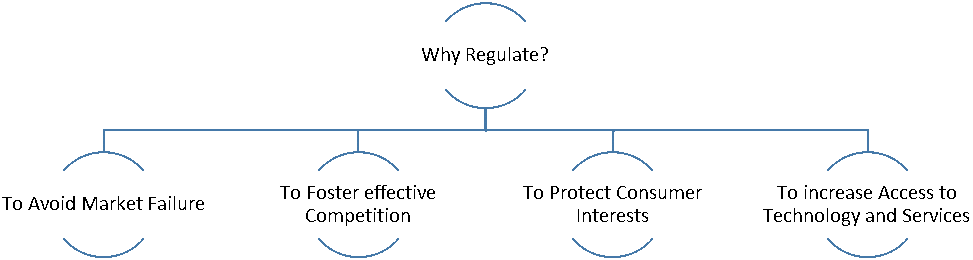
To transit to an effective, competitive environment, regulatory reform must include measures aimed at:
Below are types of our regulations available in pdf documents;